This blog was co-authored by Matthew Cheng, Senior Open RAN Manager at Vodafone.
Vodafone is a pioneer in Open RAN technologies and believes that Open RAN will lead to a more cost-effective, secure, energy efficient and customer-focused network of the future. With years of experience from multiple Open RAN tests, trials and now commercial deployments on current XR11 platforms under their belt, Vodafone has been looking at the next generation of hardware platforms that are being launched, wanting to understand how these servers will improve Open RAN performance based on real-world data.
Vodafone and Dell Technologies have been collaborating in our Open Telecom Ecosystem Lab (OTEL) to understand the load performance of Open RAN on Dell Technologies PowerEdge servers. Recently, Vodafone has been working in OTEL with the Dell Technologies engineers, conducting several iterations of qualification cycles for the next generation PowerEdge.Next servers and comparing the results with its predecessors based on real world 5G RAN systems use cases. This data has been invaluable to Vodafone, enabling them to accelerate their deployment schedule of Open RAN on the latest PowerEdge.Next servers.
We defined the engagement in OTEL between Vodafone and Dell across three phases of testing. The first phase, identified as Phase 0, focused on Layer-1 validation in a simulated environment. The next phase, Phase 1, focused on performance validation when part of a 5G end-end RAN system with real workloads driven by real world traffic models identified by Vodafone. Phase 2 focused on increasing the scale of workload testing with Vodafone traffic models. Future phases are being planned to advance deeper understanding of RAN workloads and deployment scenarios
Phase 0: Layer-1 Validation
The initial phase focused on standalone validations done with Intel’s Layer-1 FlexRAN driven by the specific real-world traffic models provided by Vodafone. FlexRAN is Intel’s reference architecture to build and deploy highly optimized, feature-rich, 4G and 5G scalable cloud-native RAN solutions. The architecture for the testing can be seen in Figure 1. The data collected in OTEL was shared across the teams to analyze various KPIs related to power efficiencies, core utilization, Forward Error Correction (FEC) offload and latencies.
The physical and logical core distribution across various software entities enabled Vodafone to gain insight into the core utilization of the XR11 PowerEdge and XR5610 PowerEdge servers and assisted Vodafone in their dimensioning exercises in how to deploy Open RAN solutions in real-world environments.
Using a data pipeline, the data collected from these tests was ingested into a data repository and used by the team to evaluate the performance of the XR11 servers versus the XR5610 servers.
Phase 1: 5G E2E Validation
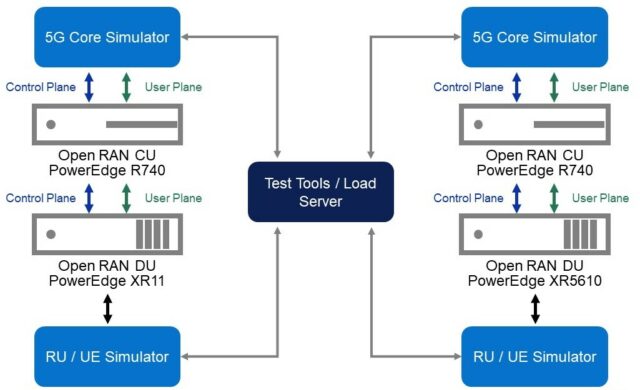
The next phase of testing focused on building an end-end RAN test-line with a real Open RAN Distributed Unit (DU) and Centralized Unit (CU) workloads connected to a simulated 5G core. The UE and Radio Unit (RU) were simulated using test tools and the high-scale load was injected based upon Vodafone traffic models. Intel FlexRAN reference software for L1 was used in the virtualized DU as part of End-to-End testing. Figure 2 shows the configuration of the test line used for the 5G end to end network.
In addition to analyzing the data collected in this phase to provide assurances of matching with the data from Phase 0, this phase also analyzed the power gains, core utilization, FEC latency, E2E latency and other KPIs based on various core allocations within the server. With Intel’s 4th Gen Xeon® Scalable processors with Intel vRAN Boost supporting up to 32 cores, the different allocation of the cores to actual Open RAN functions can be quite extensive, especially when optimizing total core utilization.
Phase 2 and Phase 3: Scale testing and PowerEdge XR8000
Phase 2 of testing focused on scale testing using traffic from a higher number of cells. These results provide closer to real-deployment power savings, aligned with Vodafone’s production system traffic model. Testing from Phase 3 would compare performance with the new flexible multi-node, short-depth, sled design testing of the PowerEdge XR8000.
Critical Learnings on Open RAN
This collaboration has generated significant learning for both Vodafone and Dell Technologies that is helping to directly incorporate efficiencies into the Open RAN offerings. As noted by Matthew Cheng, Open RAN Senior Engineer at Vodafone, “The knowledge gained collaborating with Dell Technologies and OTEL is a fundamental source of insight in decision making of current and future platforms. Leveraging Dell’s deep IT industry expertise combined with Vodafone Open RAN workload knowledge is a powerful combination to understand the impacts of the latest generation server technology on Open RAN deployments.” Vodafone has endorsed the measurements provided from OTEL and supported their 5G Open RAN deployment schedule.
To be clear, there was no silver bullet that came out of the work between OTEL and Vodafone. But the Open Telecom Ecosystem Lab and Dell Technologies engineers offer a unique set of capabilities for CSPs such as Vodafone, helping to offload much of the heavy lifting needed in building, testing, managing, analyzing and upgrading the hardware infrastructure, as well as integrating CaaS and NEP workloads, qualifying these systems and more. This allows Vodafone to focus on analyzing results with respect to their use cases, traffic models and value-additions that directly benefit their businesses.
Reach out to your Dell Technologies representative to learn how OTEL service offerings can provide a 5G infrastructure with the supporting ecosystem and serve as a common collaboration platform across your telecom partners to render benefits for your organization.


